From the sunset picture example, you have learned the importance of taking full control over the exposure on your camera. Now, it's time to dig into your camera and learn the three most basic tools available to you in controlling the exposure.
Those tools are shutter speed, aperture, and ISO. After I explain what each one does, I'll explain why we need three separate tools to control the brightness or darkness of the photo.
Aperture
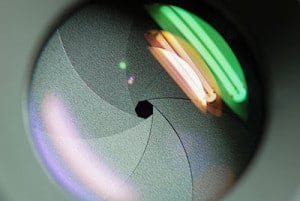
The aperture is a small set of blades in the lens that controls how much light will enter the camera. The blades create a octagonal shape that can be widened (we photogs call it shooting “wide open”), or closed down to a small hole. Obviously, if you shoot with the aperture wide open, then more light is allowed into the camera than if the aperture is closed down to only allow a tiny hole of light to enter the camera.
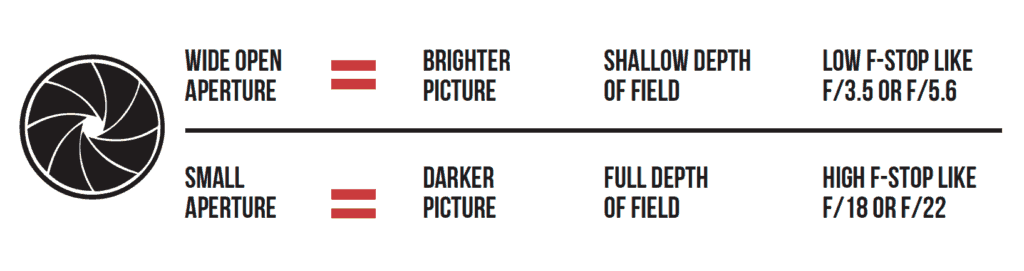
So suppose you take a picture that is too bright. How do you fix it? Simply choose a smaller aperture. Simple! Aperture sizes are measured by f-stops. A high f-stop like f-22 means that the aperture hole is quite small, and a low f-stop like f/3.5 means that the aperture is wide open.
Let's test your knowledge to make sure you have it down. If you take a picture and it's too dark at f/5.6, would you choose a lower f-stop number or a higher one? Yep! You'd choose a lower f-stop number, which opens up the aperture to let in more light. The size of the aperture controls more than the brightness or darkness of the picture, though.
The aperture also controls the depth-of-field. Depth-of-field is how much of the picture is sharp, and how much is blurry. If you want to take a picture of a person with a blurry background, you'd use shallow depth of field. If you want to take a picture of a sweeping mountain vista, you'd want to use a small aperture size (high f-stop number) so that the entire scene is in sharp focus. If you, like me, are more of a visual learner, then I think this graphic will help solidify the information about aperture. Take a minute and make sure you understand this info before moving on.
Shutter Speed
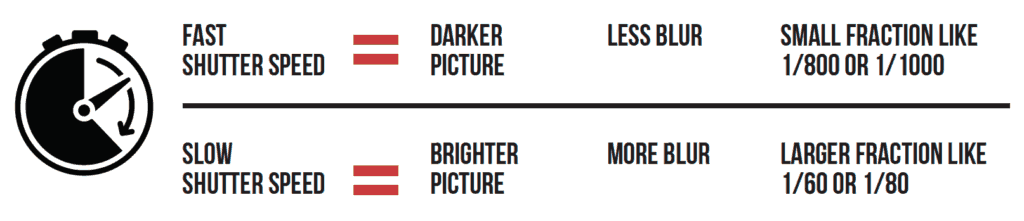
The shutter is a small “curtain” in the camera that quickly rolls over the image sensor (the digital version of film) and allows light to shine onto the imaging sensor for a fraction of a second. The longer the shutter allows light to shine onto the image sensor, the brighter the picture since more light is gathered. A darker picture is produced when the shutter moves very quickly and only allows light to touch the imaging sensor for a tiny fraction of a second. The duration that the shutter allows light onto the image sensor is called the shutter speed, and is measured in fractions of a second. So a shutter speed of 1/2 of a second will allow more light to touch the image sensor and will produce a brighter picture than a shutter speed of 1/200 of a second. So if you're taking a picture and it is too dark, you could use a slower shutter speed to allow the camera to gather more light.

Just as the aperture affects the exposure as well as the depth-of field, the shutter affects more than just the exposure. The shutter speed is also principally responsible for controlling the amount of blur in a picture. If you think about it, it makes sense that the shutter speed controls how much blur is in the picture.
Imagine me sitting here at my computer desk waving to you (you don't have to imagine very hard if you just look at the picture on the right). If you take a picture of me with a shutter speed of 1/30th of a second, then my hand will have moved in the time that the camera is recording the picture. To get rid of the blur, you need to increase the shutter speed to around 1/320th of a second. At this speed, my hand is still moving, but the camera takes the picture so fast that my hand travels only such a small distance that it is not noticeable in the picture.
The next question that most people ask is, how slow of a shutter speed can you use and still get a sharp picture? My blog post on Minimum Shutter Speeds will answer your question!
ISO
The funny thing about ISO is that it is an acronym, but nobody really knows what it stands for. It is always just called ISO even though it really stands for International Organization for Standardization. Every once in a while, you'll hear an older photographer pronounce it “I-so”, but almost everyone pronounces it “I.S.O.” The ISO controls the exposure by using software in the camera to make it extra sensitive to light.
A high ISO such as ISO 1,600 will produce a brighter picture than a lower ISO such as ISO 100. The drawback to increasing the ISO is that it makes the picture noisier. Digital noise is apparent when a photo looks grainy. Have you ever taken a picture at night with your cell phone or your pocket camera, and noticed that it looks really grainy? That is because the camera tried to compensate for the dark scene by choosing a high ISO, which causes more grain.
What constitutes a “high” ISO is constantly changing. Camera companies are constantly improving the ability of cameras to use high ISOs without as much grain. A few years ago, only the highest-end pro DSLR cameras could achieve 2,000 ISO, and now even entry-level DSLR cameras can shoot at this level. Since each camera is different, you would do well to do a few tests with your camera to see how high of an ISO you can shoot at without making the image overly grainy.
Right now, you will commonly find new DSLRs that advertise expandable ISO ranges.
Putting It All Together
I know exactly what you're thinking. “Why do I need three tools to control the exposure? Wouldn't one suffice?” The answer is no, and I'll explain why with an example. In January, I took a trip to my favorite place on the planet to take pictures–Yellowstone National Park. My guide informed us that the bighorn sheep in the park were dying off very quickly due to whooping cough, so I worked hard that week to capture pictures of the last few sheep in that area of the park.
Around 9AM on a cloudy day, I found a small group of bighorn sheep and started photographing them with a long 600mm lens. The early hour and clouded sky made the situation quite dark for shooting.
Let me help you out. The lens I was working with cost around $12,000, but don’t worry. You can get really good results with a much more affordable 600mm lens. I’m considering selling my expensive lens.
Anyway, it had a maximum aperture size of f/4. So I set my aperture at f/4 to gather as much light as possible. This also impacted the depth-of field to blur out the rocks behind the bighorn sheep. Next, I set my shutter speed. I wanted to capture action in the photo, so I set my camera to 1/1000th of a second shutter speed. I knew that this fast of a shutter speed would prevent any motion blur from the sheep running on the mountain side. Then, I took a picture. WAAAY too dark! I couldn't compromise my shutter speed or aperture, so I knew I needed to use the third player in the exposure triangle–the ISO.
I played around with my ISO and found that if I increased it to ISO 640, it made the picture bright enough to take the picture without making it overly grainy. This combination of shutter speed, aperture, and ISO worked out perfectly. It feels so good to hone in the camera settings!
Now can you see why you need to know how to shutter, aperture, AND ISO, and know how to set them independently on your camera!
If you're a visual learner and want to really learn your camera, then be sure to check out my Photography Start Course. Just a reminder, it's a series of 22 videos where I take you on location to shoot waterfalls, landscapes, people, kids, and macro photos. You can look over my shoulder and see exactly how I set up my camera to take professional photos.
Now, you need to learn how to apply these settings on your camera to take advantage of your new-found nuggets of knowledge.




Hi Sir,
I’m a newbie int this field & I shot mostly auto. I really want to try manual, but I failed many times.
From your article, it seems like the first rule to set up is Aperture, then tone down to shutter speed and lastly ISO?
Which normally would you do sir?
Btw great articles. All your articles helped me in understanding the basic rules.
Thank you.
Tnx…….brother. ..love you….you have understand me lot….now umm. . Improving. …lot tnx to u?❤ brother
This was incredibly easy to understand and very helpful. Jim, you are amazing and your pictures really inspire me to pursue photography.
It’s very helpful but very long vut I will try my best to keep it up….I’m only 13 but my dream is to become a vet and photographer….and with your notes this is very helpful thank you!!!!??
Thanks a lot… I got full information abt the basics Now I m going to start and will have a better pic
From this article i got the thorough knowledge of camera, on the basis of which now i am able to choose a good camera phone. thanks allot.
Can I simply just say what a relief to uncover someone who actually understands what they’re talking about online. You definitely realize how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More and more people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I was surprised you are not more popular given that you most certainly have the gift.
THANKS SO MUCH,I HV BEEN ENLIGHTENED
Much appreciate the well written explanation! An example really helps memories the difference.
Thanks a lot. It was really insightful and straightforward.
Thanks a lot. It was really helpful to me. I really enjoy reading articles on this blog. And, this one cleared many of my doubts on shutter speed and ISO
You can see our latest offers in out website:
Thanks Jim!! This is great information! Can’t wait to start applying these techniques!
Hi Kim! Good to hear from you. How is Rexburg? Hope you and Clegg are well.
Hi there. I came across your website recently and I’m finding it very helpful. I appreciate you helping people like myself who are amateur photographers.
I just bought a Canon EOS Rebel SL1. I’m using your printable quick guide for various photography settings and I’m confused about the Av setting and shutter speed. On my camera, when it is in Av mode, the shutter speed setting goes away and I am not able to adjust it. Am I missing something?
Thank you in advance for your help and advice.
very usefull knowledge. thank you very much sir. Let me to print this for my note and i hope will remember this lesson
Please Lemme know the Best settings for evening (Low Light ) and night photography in Canon EOS 1200D.
I need to know urgently.
One more query, am unable to set the f/no below 5.6 in AV mode.
I have gone through more than 50 tutorials…
But this is the very clear about each parts
thank you
As much as I know about photography, it has all come from a hobby to professional, and self taught. Which makes me nervous anytime I have a shoot. I have to remind myself that I can do it and make a mental checklist on everything I need to look at. One of the hardest things for me to master has been the dreaded triangle. I figured out the ISO, next was the Aperture, but the Shutter Speed confused me. I liked the way you explained it, and the simple charts. This will help me keep it in my brain. Thank you.
Very well explained! Thank You!
Thanks for clarifying the differences between ISO, aperture, and shutter speed. I have read the same info elsewhere but this was much easier to follow.